DNS
DNS - Domain Name System
DNS is like a directory which links the domain name to the IP address of the server
- google.com <> 216.58.197.78
- facebook.com <> 173.252.89.132
Every server must have a unique IP address which clients can use to connect with it over the internet
This IP address is mapped to a human friendly domain name to make it easy to remember
The directory is maintained by “name servers”. Programs can exchange the domain-name for the registered IP address by requesting the name server. This is called a “DNS lookup”
Example: When a client requests a website (e.g., www.educative.io), the internet browser installed on the client’s computer interacts through IP addresses. The job of the DNS is to translate the domain names to IP addresses so that the browser can load the requested internet resource 👇
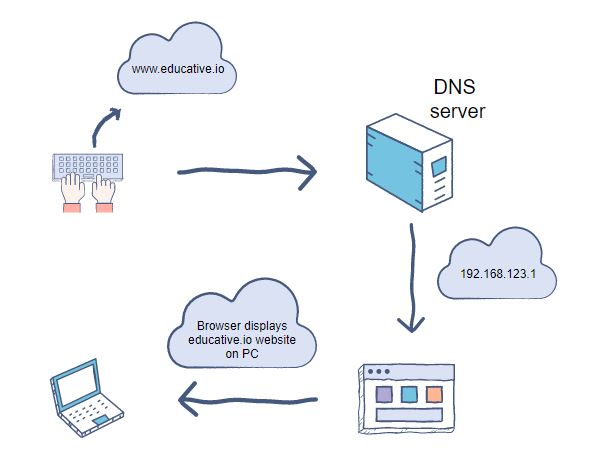
How DNS works
- The user enters the domain (website) name and the browser checks its memory to see if the relevant IP address is already stored
- If the IP address is not stored in the computer’s local memory (also known as cache memory), then the browser reaches out to the DNS server and checks for the domain name there. If it is found, then the DNS sends the exact IP address of that domain name back to the browser
- Once the IP address reaches the computer, the browser finds it on the internet. The browser then communicates with the domain name being hosted to request the associated files. The host server returns the files that display educative.io in the user’s web browser
- If the domain name is not found, the DNS server returns error 404 (webpage not found)