Graph
Graph
What is a graph?
In programming, a graph is a common data structure that consists of a finite set of nodes (or vertices) and edges. The edges connect the vertices to form a network. An edge can be uni-directional or bi-directional. Edges are also known as arrows in a directed graph and may contain values that show the required cost to traverse from one vertex to another.
Types of graphs
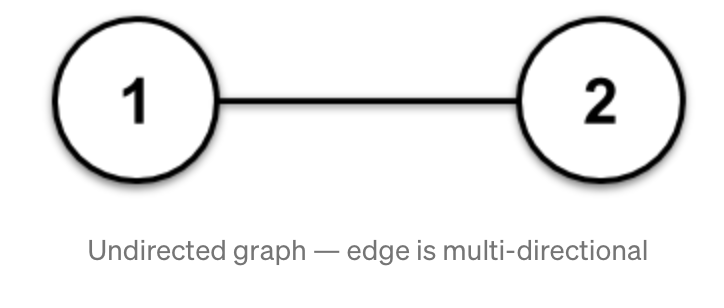
1. Undirected graph:
In an undirected graph, an edge connects two nodes in both directions as a two-way street does.
function Edge(src, dest){
this.src = src;
this.dest = dest;
}
const Graph = function(edges){
// A list of lists to represent an adjacency list
let adj = new Map();
// add edges to the directed graph
for (let current of edges) {
// allocate new node in adjacency list from src to dest
const {src, dest} = current;
if(adj.has(src)){
adj.get(src).push(dest);
}else{
adj.set(src, [dest]);
}
// uncomment next lines for undirected graph
// allocate new node in adjacency list from dest to src
if(adj.has(dest)){
adj.get(dest).push(src);
}else{
adj.set(dest, [src]);
}
}
this.add = function(edge) {
const {src, dest} = edge;
if(adj.has(src)){
adj.get(src).push(dest);
}else{
adj.set(src, [dest]);
}
// uncomment next lines for undirected graph
// allocate new node in adjacency list from dest to src
if(adj.has(dest)){
adj.get(dest).push(src);
}else{
adj.set(dest, [src]);
}
}
this.remove = function(edge) {
const {src, dest} = edge;
let srcList = adj.get(src);
srcList = srcList.filter(e => e !== dest);
if(srcList.length === 0){
adj.delete(src);
}else{
adj.set(src, srcList);
}
// uncomment next lines for undirected graph
let destList = adj.get(dest);
destList = destList.filter(e => e !== src);
if(destList.length === 0){
adj.delete(dest);
}else{
adj.set(dest, destList);
}
return true;
}
this.print = function() {
let n = adj.size;
for (let src of adj.keys()) {
// print current vertex and all its neighboring vertices
let str = "";
for (let dest of adj.get(src)) {
str += "(" + src + " ——> " + dest + ")";
}
console.log(str);
}
}
//Return graph
this.getList = () => adj;
}
Input:
const arr = [new Edge(0, 1), new Edge(2, 0),
new Edge(2, 1), new Edge(3, 2),
new Edge(4, 5), new Edge(5, 4)];
const graph = new Graph(arr);
graph.add(new Edge('c', 'd'));
graph.print();
Output:
"(0 ——> 1)(0 ——> 2)"
"(1 ——> 0)(1 ——> 2)"
"(2 ——> 0)(2 ——> 1)(2 ——> 3)"
"(3 ——> 2)"
"(4 ——> 5)(4 ——> 5)"
"(5 ——> 4)(5 ——> 4)"
"(c ——> d)"
"(d ——> c)"
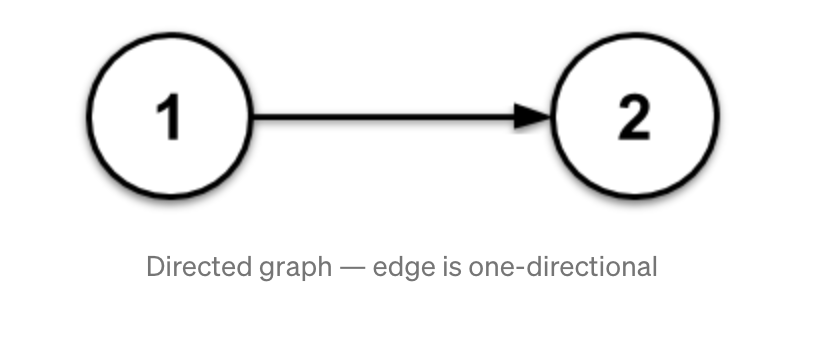
2. Directed graph:
A directed graph only has directed edges. They can be imagined like a one-way street. If an edge leads from n1 to n2 it does not also lead from n2 to n1.
/*Directed graph*/
function Edge(src, dest){
this.src = src;
this.dest = dest;
}
const Graph = function(edges){
// A list of lists to represent an adjacency list
let adj = new Map();
// add edges to the directed graph
for (let current of edges) {
// allocate new node in adjacency list from src to dest
const {src, dest} = current;
if(adj.has(src)){
adj.get(src).push(dest);
}else{
adj.set(src, [dest]);
}
}
this.add = function(edge) {
const {src, dest} = edge;
if(adj.has(src)){
adj.get(src).push(dest);
}else{
adj.set(src, [dest]);
}
}
this.remove = function(edge) {
const {src, dest} = edge;
let srcList = adj.get(src);
srcList = srcList.filter(e => e !== dest);
if(srcList.length === 0){
adj.delete(src);
}else{
adj.set(src, srcList);
}
return true;
}
this.print = function() {
let n = adj.size;
for (let src of adj.keys()) {
// print current vertex and all its neighboring vertices
let str = "";
for (let dest of adj.get(src)) {
str += "(" + src + " ——> " + dest + ")";
}
console.log(str);
}
}
//Return graph
this.getList = () => adj;
}
Input:
const arr = [new Edge(0, 1), new Edge(1, 2),
new Edge(2, 0), new Edge(2, 1), new Edge(3, 2),
new Edge(4, 5), new Edge(5, 4)];
const graph = new Graph(arr);
graph.add(new Edge('c', 'd'));
graph.print();
Output:
"(0 ——> 1)"
"(1 ——> 2)"
"(2 ——> 0)(2 ——> 1)"
"(3 ——> 2)"
"(4 ——> 5)"
"(5 ——> 4)"
"(c ——> d)"