Hash Tables
Hash Tables
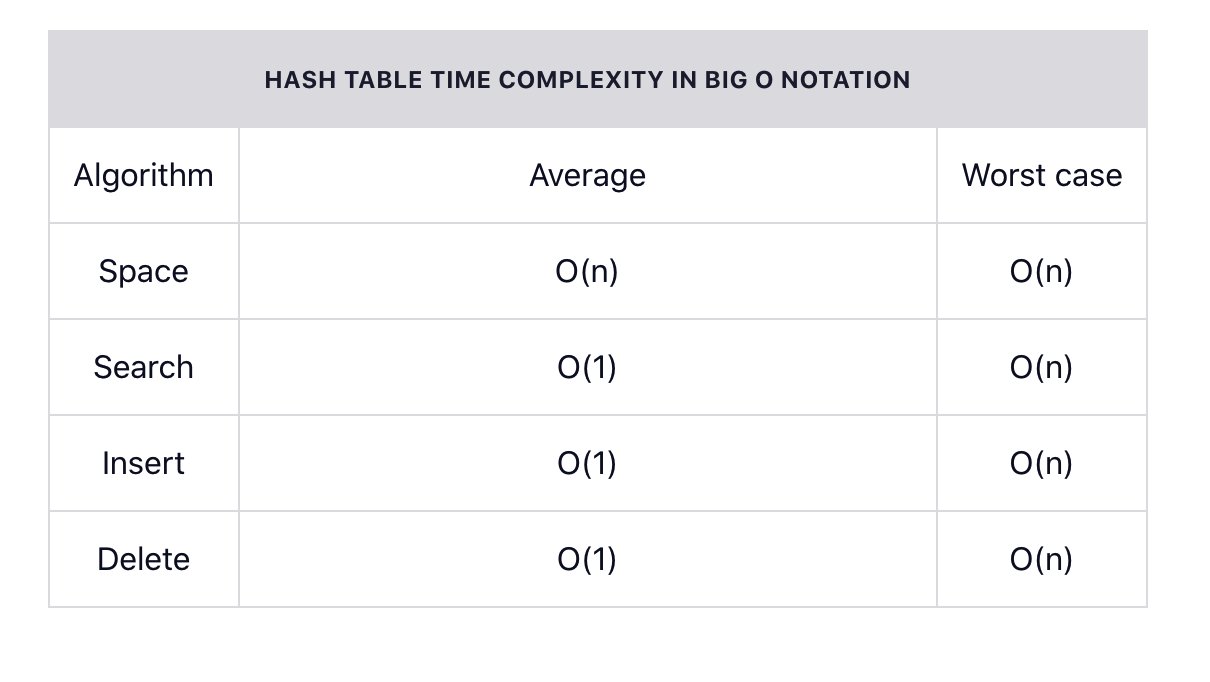
Has tables is used to implement associative arrays or mappings of key value pairs. Hash tables are a common way to implement the map data structure or objects they are widely used because of how efficient they are. The average time for each lookup is not tied to the number of elements stored in the table. the average time complexity of hash tables and big O of 1 for a search insert and delete. example shown in below table.
You’ll commonly use a Hash table because of its fast search, insertion, and delete operation:
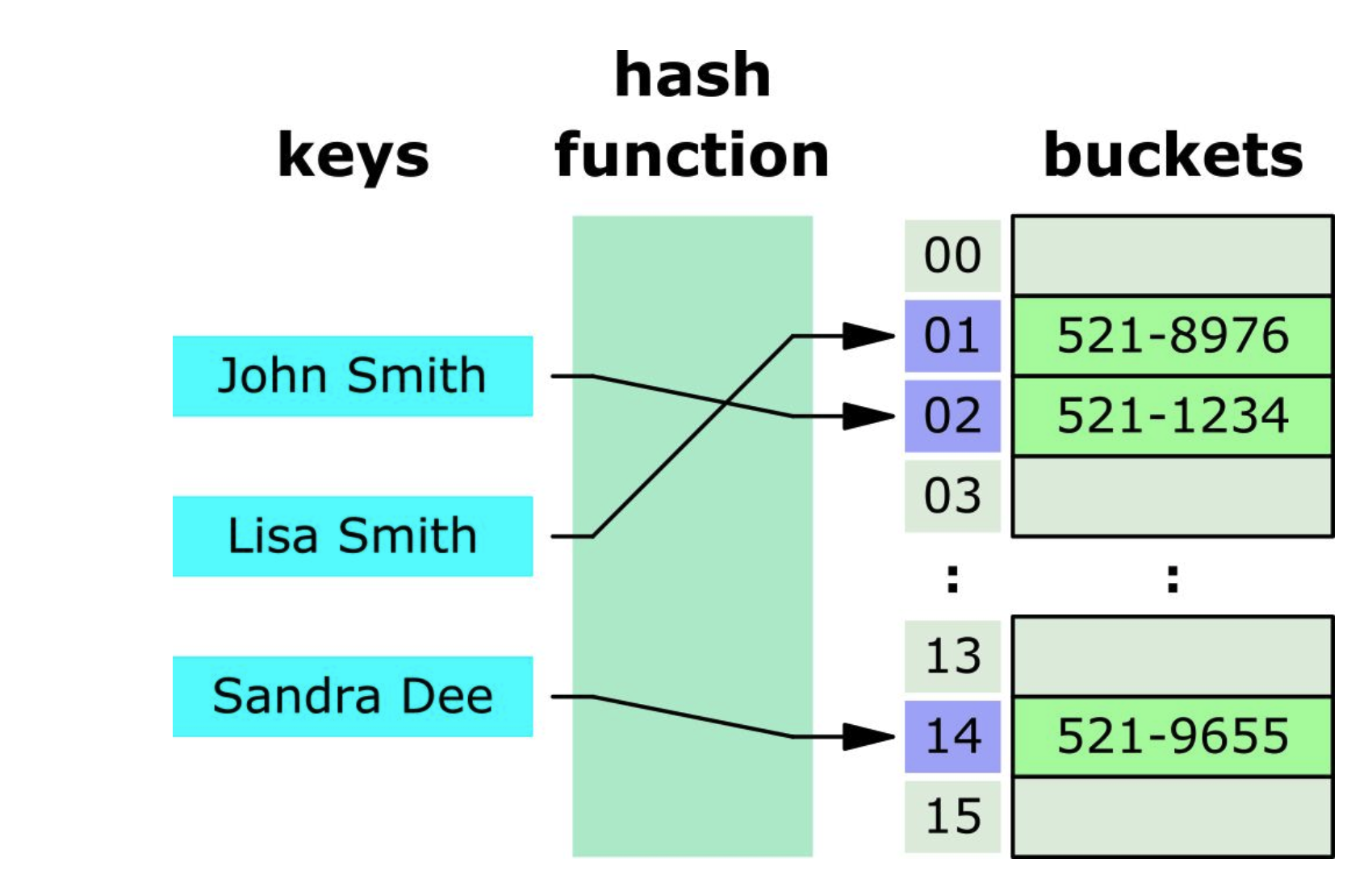
The way hash table works:
It takes a key input and then runs it through a hash function. A hash function basically just map string to numbers and usually the numbers just correspond to indexes in an array.
A hash function needs to be consistent so when you run a key through the hash function, it always gives same number and it should map different words to different numbers.
If two words get hashed the same number this is called a collision.
Creating a hash table using javascript
You can implement a Hash Table in JavaScript in three steps:
- Create a
HashTableclass withtableandsizeinitial properties - Add a
hash()function to transform keys into indices - Add the
set()andget()methods for adding and retrieving key/value pairs from the table.
Alright, let’s start with creating the HashTable class. The code below will create a table of buckets with the size of 127:
class HashTable {
constructor() {
this.table = new Array(127);
this.size = 0;
}
}
How to write the hash() method
Next, you need to create the hash() method that will accept a key value and transform it into an index.
A simple way to create the hash would be to sum the ASCII code of the characters in the key using the charCodeAt() method as follows. Note that the method is named using _ to indicate that it’s a private class
To ensure that the hash value doesn’t exceed the bucket size, you need to use the modulo operator as shown below:
_hash(key) {
let hash = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < key.length; i++) {
hash += key.charCodeAt(i);
}
return hash % this.table.length;
}
How to write the set() method
To set the key/value pair in your Hash Table, you need to write a set() method that accepts (key, value) as its parameters:
- The
set()method will call the_hash()method to get theindexvalue. - The
[key, value]pair will be assigned to thetableat the specifiedindex - Then, the
sizeproperty will be incremented by one
set(key, value) {
const index = this._hash(key);
this.table[index] = [key, value];
this.size++;
}
How to write the get() method
To get a certain value from the Hash Table, you need to write a get() method that accepts a key value as its parameter:
- The method will call the
_hash()method to once again retrieve the tableindex - Return the value stored at
table[index]
get(key) {
const index = this._hash(key);
return this.table[index];
}
How to write the remove() method
To delete a key/value pair from the Hash Table, you need to write a remove() method that accepts a key value as its parameter:
- Retrieve the right
indexusing the_hash()method - Check if the
table[index]has a truthy value and thelengthproperty is greater than zero. Assign theundefinedvalue to the rightindexand decrement thesizeproperty by one if it is. - If not, simply return
false
remove(key) {
const index = this._hash(key);
if (this.table[index] && this.table[index].length) {
this.table[index] = undefined;
this.size--;
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
Here’s the full code for the Hash Table implementation again:
class HashTable {
constructor() {
this.table = new Array(127);
this.size = 0;
}
_hash(key) {
let hash = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < key.length; i++) {
hash += key.charCodeAt(i);
}
return hash % this.table.length;
}
set(key, value) {
const index = this._hash(key);
this.table[index] = [key, value];
this.size++;
}
get(key) {
const target = this._hash(key);
return this.table[target];
}
remove(key) {
const index = this._hash(key);
if (this.table[index] && this.table[index].length) {
this.table[index] = [];
this.size--;
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
}
//To test the HashTable class, I'm going to create a new instance of the class and set some key/value pairs as shown below.
const ht = new HashTable();
ht.set("Canada", 300);
ht.set("France", 100);
ht.set("Spain", 110);
//Then, let's try to retrieve them using the get() method:
console.log(ht.get("Canada")); // [ 'Canada', 300 ]
console.log(ht.get("France")); // [ 'France', 100 ]
console.log(ht.get("Spain")); // [ 'Spain', 110 ]