Linked List
Linked List
What is a Linked List?
A linked list is a linear data structure similar to an array. However, unlike arrays, elements are not stored in a particular memory location or index. Rather each element is a separate object that contains a pointer or a link to the next object in that list.
Each element (commonly called nodes) contains two items: the data stored and a link to the next node. The data can be any valid data type. You can see this illustrated in the diagram below.
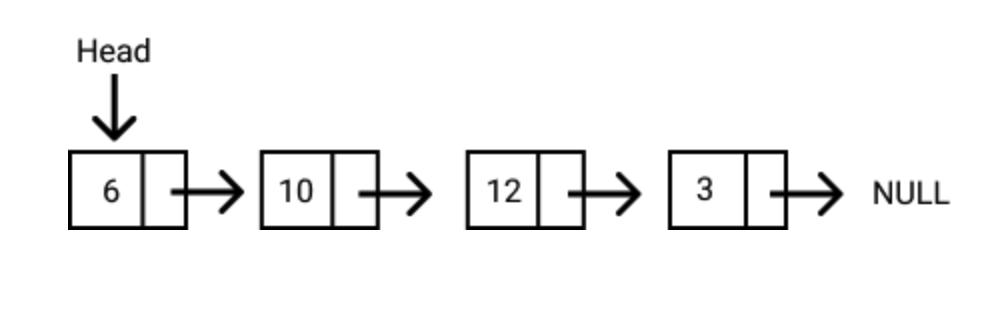
The entry point to a linked list is called the head. The head is a reference to the first node in the linked list. The last node on the list points to null. If a list is empty, the head is a null reference.
In JavaScript, a linked list looks like this:
const list = {
head: {
value: 6
next: {
value: 10
next: {
value: 12
next: {
value: 3
next: null
}
}
}
}
}
};
Types of Linked Lists
There are three types of linked lists:
- Singly Linked Lists: Each node contains only one pointer to the next node. This is what we have been talking about so far.
- Doubly Linked Lists: Each node contains two pointers, a pointer to the next node and a pointer to the previous node.
- Circular Linked Lists: Circular linked lists are a variation of a linked list in which the last node points to the first node or any other node before it, thereby forming a loop.
Implementing a Linked List in JavaScript
The code below shows the implementation of a linked list class with a constructor. Notice that if the head node is not passed, the head is initialised to null.
class LinkedList {
constructor(head = null) {
this.head = head
}
}
Putting it all together
Let’s create a linked list with the class we just created. First, we create two list nodes, node1 and node2 and a pointer from node 1 to node 2.
let node1 = new ListNode(2)
let node2 = new ListNode(5)
node1.next = node2
Next, we’ll create a Linked list with the node1.
let list = new LinkedList(node1)
//Let's try to access the nodes in the list we just created.
console.log(list.head.next.data) //returns 5
Some LinkedList methods
Next up, we will implement four helper methods for the linked list. They are:
- size()
- clear()
- getLast()
- getFirst()
1. size()
This method returns the number of nodes present in the linked list.
size() {
let count = 0;
let node = this.head;
while (node) {
count++;
node = node.next
}
return count;
}
2. clear()
This method empties out the list.
clear() {
this.head = null;
}
3. getLast()
This method returns the last node of the linked list.
getLast() {
let lastNode = this.head;
if (lastNode) {
while (lastNode.next) {
lastNode = lastNode.next
}
}
return lastNode
}
4. getFirst()
This method returns the first node of the linked list.
getFirst() {
return this.head;
}